Mutation Query
| | | | Allele 1: | K601E | | Allele 2: | D122Y, Q1236H, Y837C | Allelic information known | | Refine query |
|
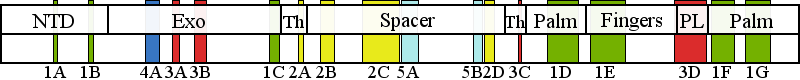
| | | Residue D122 | | Cluster assignment: | | | Cluster description: | Single Nucleotide Polymorphism | | POLG domain: | N-Terminal domain |
| Residue K601 | | Cluster assignment: | | | Cluster description: | Upstream DNA binding channel | | Subcluster: | 2C (residues 561-617) | | Subcluster description: | Subcluster 2C contains motif 1, which in Pol I was shown to fold into a loop that binds DNA in the channel (Loh and Loeb, 2005). Motif 1, together with subcluster 2D, form the major face of the putative DNA binding channel. | | POLG domain: | Spacer domain |
| Residue Y837 | | Cluster assignment: | | | Cluster description: | Single Nucleotide Polymorphism | | POLG domain: | Polymerase domain |
| Residue Q1236 | | Cluster assignment: | | | Cluster description: | Single Nucleotide Polymorphism | | POLG domain: | Polymerase domain |
|
|
Mutation Information
|
| K601E | | | | Number of patients: (with K601E) | 2 | | Found together with: | |  | Show Patient Data |
| Patient data are sorted by mutation combination frequency. | Reference: | Zabalza et al, 2014; | | Description: | Unsteady walk, and showed tremor in both legs when standing. Difficulty in concentrating. Dysarthria. No deep tendon reflexes were evident. Sensory axonal neuropathy. Hyperintensities in images of the subcortical frontal and temporal white substances. myoclonia and tonic-clonic seizures. sensory axonal neuropathy in the lower limbs, moderate dysarthria, and an ataxic gait. | | Mutations: | K601E | | SNPs: | D122Y, Q1236H, Y837C | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 56, Age of Patient: 61, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Zabalza et al, 2014; | | Description: | ataxia, dysarthria and sensory axonal polyneuropathy. At age 52, the patient developed instability upon walking and paraesthesia in lower limbs, when no other symptoms were apparent. Clinical examination at age 67 revealed dysarthria, gait ataxia, hyporeflexia and tactile hypoestesia. Atrophy of the cerebellar hemispheres. Cognitive decline. left hemiparesis related to a non-traumatic subdural haematoma that required neurosurgical treatment, and began to experience myoclonus and tonic-clonic seizures. weak bilateral palpebral ptosis. | | Mutations: | K601E | | SNPs: | D122Y, Q1236H, Y837C | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 52, Age of Patient: 67, Age of Death: n/a |
|
| D122Y | | | | Number of patients: (with D122Y) | 2 | | Found together with: | |  | Show Patient Data |
| Patient data are sorted by mutation combination frequency. | Reference: | Zabalza et al, 2014; | | Description: | Unsteady walk, and showed tremor in both legs when standing. Difficulty in concentrating. Dysarthria. No deep tendon reflexes were evident. Sensory axonal neuropathy. Hyperintensities in images of the subcortical frontal and temporal white substances. myoclonia and tonic-clonic seizures. sensory axonal neuropathy in the lower limbs, moderate dysarthria, and an ataxic gait. | | Mutations: | K601E | | SNPs: | D122Y, Q1236H, Y837C | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 56, Age of Patient: 61, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Zabalza et al, 2014; | | Description: | ataxia, dysarthria and sensory axonal polyneuropathy. At age 52, the patient developed instability upon walking and paraesthesia in lower limbs, when no other symptoms were apparent. Clinical examination at age 67 revealed dysarthria, gait ataxia, hyporeflexia and tactile hypoestesia. Atrophy of the cerebellar hemispheres. Cognitive decline. left hemiparesis related to a non-traumatic subdural haematoma that required neurosurgical treatment, and began to experience myoclonus and tonic-clonic seizures. weak bilateral palpebral ptosis. | | Mutations: | K601E | | SNPs: | D122Y, Q1236H, Y837C | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 52, Age of Patient: 67, Age of Death: n/a |
|
| Q1236H | | | | Number of patients: (with Q1236H) | 12 | | Found together with: | PNF=Putatively Non-Functional enzyme |  | Show Patient Data |
| Patient data are sorted by mutation combination frequency. | Reference: | Horvath et al, 2006; | | Description: | Onset at 2 years with encephalopathy, hepatopathy, and myoclonus achalasia. Diagnosed as Alpers. | | Mutations: | R1096C, R1096C | | SNPs: | Q1236H, Q1236H | | Age group: | infantile | | Age of Onset: 2, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Wong et al, 2008; | | Description: | developmental delay, dementia, seizures, Alpers, Family history of Alpers syndrome. | | Mutations: | R1096C, R1096C | | SNPs: | Q1236H, Q1236H | | Age group: | infantile | | Age of Onset: 1, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Luoma et al, 2005; | | Description: | Developed bilateral blepharoptosis in his youth. Neurological examination at the age of 72 showed severe blepharoptosis, lids almost covering his entire pupils. Eye movements were normal, his muscle strength and sensation were good and tendon reflexes were normal, but his gait was unsteady. Early onset ptosis, ataxia | | Mutations: | R627Q | | SNPs: | Q1236H | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 22, Age of Patient: 73, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Luoma et al, 2005; | | Description: | developed progressive blepharoptosis at the age of 20 and ophthalmoplegia during subsequent years, at 35, the patient developed progressive unsteadiness of gait. She noted fatigue, myalgia and cramps, which were triggered by moderate exercise. At 44, restless legs syndrome, deficits in memory and concentration, and suffered from recurrent episodes of depression, at 46 showed bilateral blepharoptosis, limited eye movements in all directions except downwards, lateral rotatory nystagmus and slight upbeat nystagmus in upward gaze, but no saccades. She had facial muscle weakness, dysarthria and slight proximal muscle weakness. She had glove and stockinglike hypoesthesia, distally impaired vibration sense, absent ankle reflexes and weak other tendon reflexes, as well as mild dysmetria. Her gait was broad-based, with further impairment with eyes closed. Tandem gait was impaired. deltoid muscle showed myopathic features, structurally abnormal mitochondria with para-crystalline inclusions, | | Mutations: | A467T, R627Q | | SNPs: | Q1236H | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 20, Age of Patient: 46, Age of Death: n/a |
Back to top | Reference: | Luoma et al, 2005; | | Description: | displays mild bilateral blepharoptosis and slight unsteadiness during tandem gait. Early onset ptosis, ataxia | | Mutations: | R627Q | | SNPs: | Q1236H | | Age group: | juvenile | | Age of Onset: n/a, Age of Patient: 19, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Zabalza et al, 2014; | | Description: | Unsteady walk, and showed tremor in both legs when standing. Difficulty in concentrating. Dysarthria. No deep tendon reflexes were evident. Sensory axonal neuropathy. Hyperintensities in images of the subcortical frontal and temporal white substances. myoclonia and tonic-clonic seizures. sensory axonal neuropathy in the lower limbs, moderate dysarthria, and an ataxic gait. | | Mutations: | K601E | | SNPs: | D122Y, Q1236H, Y837C | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 56, Age of Patient: 61, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Zabalza et al, 2014; | | Description: | ataxia, dysarthria and sensory axonal polyneuropathy. At age 52, the patient developed instability upon walking and paraesthesia in lower limbs, when no other symptoms were apparent. Clinical examination at age 67 revealed dysarthria, gait ataxia, hyporeflexia and tactile hypoestesia. Atrophy of the cerebellar hemispheres. Cognitive decline. left hemiparesis related to a non-traumatic subdural haematoma that required neurosurgical treatment, and began to experience myoclonus and tonic-clonic seizures. weak bilateral palpebral ptosis. | | Mutations: | K601E | | SNPs: | D122Y, Q1236H, Y837C | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 52, Age of Patient: 67, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Taanman et al, 2009; | | Description: | Hypotonia at 8 weeks, seizures, hepatopathy, lactic acidemia, died of liver failure. 9% mtDNA copy number in muscle, 11% mtDNA copy number in liver. | | Mutations: | H1110Y, W748S | | SNPs: | E1143G, Q1236H | | Age group: | infantile | | Age of Onset: 0.1, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: 0.8 |
| Reference: | Pagnamenta et al, 2006; | | Description: | Presented with ptosis and PEO, in early 20’s, premature ovarian failure at 28 years. proximal muscle weakness, exertional dyspnoea and sensory ataxia, Peripheral neuropathy | | Mutations: | Y955C | | SNPs: | Q1236H | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 22, Age of Patient: 33, Age of Death: n/a |
Back to top | Reference: | Luoma et al, 2007; | | Description: | Parkinsons disease, tremor, rigidity, hypo-/ bradykinesia. | | Mutations: | | | SNPs: | Q1236H, R722H | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 66, Age of Patient: 77, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Luoma et al, 2007; | | Description: | Parkinsons disease, tremor, rigidity, hypo-/ bradykinesia. Ischemic Heart Disease, atrial fibrillation, hypertension | | Mutations: | | | SNPs: | Q1236H, Y831C | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 70, Age of Patient: 79, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Wong et al, 2008; | | Description: | Alpers, chorea, microcephaly, leukodystrophy, Seizures, Dementia, developmental delay. | | Mutations: | A467T | | SNPs: | PNF, Q1236H | | Age group: | infantile | | Age of Onset: 1.5, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: n/a |
|
| Y837C | | | | Number of patients: (with Y837C) | 2 | | Found together with: | |  | Show Patient Data |
| Patient data are sorted by mutation combination frequency. | Reference: | Zabalza et al, 2014; | | Description: | Unsteady walk, and showed tremor in both legs when standing. Difficulty in concentrating. Dysarthria. No deep tendon reflexes were evident. Sensory axonal neuropathy. Hyperintensities in images of the subcortical frontal and temporal white substances. myoclonia and tonic-clonic seizures. sensory axonal neuropathy in the lower limbs, moderate dysarthria, and an ataxic gait. | | Mutations: | K601E | | SNPs: | D122Y, Q1236H, Y837C | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 56, Age of Patient: 61, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Zabalza et al, 2014; | | Description: | ataxia, dysarthria and sensory axonal polyneuropathy. At age 52, the patient developed instability upon walking and paraesthesia in lower limbs, when no other symptoms were apparent. Clinical examination at age 67 revealed dysarthria, gait ataxia, hyporeflexia and tactile hypoestesia. Atrophy of the cerebellar hemispheres. Cognitive decline. left hemiparesis related to a non-traumatic subdural haematoma that required neurosurgical treatment, and began to experience myoclonus and tonic-clonic seizures. weak bilateral palpebral ptosis. | | Mutations: | K601E | | SNPs: | D122Y, Q1236H, Y837C | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 52, Age of Patient: 67, Age of Death: n/a |
|
|
|
|
The following information is based on PON-P2 mutation pathogenicity prediction software results. Cluster 2 mutation with a non-cluster-mapping mutation (SNP) Y837C | PON-P2 predictions results for Y837C | | Pathogenicity: | Pathogenic | | Probability: | 0.903 | | Standard Error: | 0.039 | | Prediction result is based on sequence analysis only and may not be accurate. |
Risk of POLG-related syndromes exists.
Mutation pathogenicity prediction suggests that this mutation could be pathogenic. Predicted chance of pathogenicity is 90.3%. See further details for residue 837. All mutations mapping into the pathogenic clusters are in high risk of being pathogenic. As a rule, a patient must have a pathogenic mutation in both of his/ her POLG genes to develop a POLG-related syndrome. |
|