Mutation Query
| | | | Allele 1: | P648R | | Allele 2: | R807C | Allelic information known | | Refine query |
|
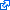
| | | Residue P648 | | Cluster assignment: | | | Cluster description: | Putative protein-protein interactions | | Subcluster: | 5A (residues 623-648) | | Subcluster description: | Located in the periphery of the IP subdomain of the spacer domain, distant from the DNA binding channel | | POLG domain: | Spacer domain |
| Residue R807 | | Cluster assignment: | | | Cluster description: | Partitioning loop | | Subcluster: | 3C (residues 795-807) | | Subcluster description: | A segment of the thumb subdomain of the pol domain located on the inner face of the DNA binding channel between the pol and exo active sites | | POLG domain: | Polymerase domain |
|
|
Mutation Information
|
| P648R | | | | Number of patients: (with P648R) | 7 | | Found together with: | PNF=Putatively Non-Functional enzyme |  | Show Patient Data |
| Patient data are sorted by mutation combination frequency. | Reference: | Ferreira et al, 2011; | | Description: | Onset at 39 years with SANDO. | | Mutations: | P648R, R807C | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 39, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Gago et al, 2006; | | Description: | Man presented at age 39 progressive bilateral ptosis, unsteadiness gait and muscle weakness with difficulty in dressing and lifting objects. Three years later he noticed dysphagia and diplopia and sought medical advice. Neurological examination revealed droopy eyes which worsened after repeated eye movements and external ophthalmoparesis with diplopia on horizontal gaze. The patient also presented fluctuant dysarthria and dysphagia which worsened at the end of the day. There was distal limb muscles weakness with reduced deep tendon reflexes. Perception of vibration and position was absent below the iliac crests. Touch, pain and temperature senses were preserved. Signs of cerebellar dysfunction were also evident. Romberg sign was positive. multiple mtDNA deletions in muscle Summary: Sensory ataxia with neuropathy, dysarthria and ophthalmoparesis represent the clinical triad of SANDO | | Mutations: | P648R, R807C | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 39, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: 44 |
| Reference: | Miguel et al, 2014; | | Description: | progressive bilateral ptosis, unsteadiness gait and muscles weakness at the age of 39 and developed dysphagia and diplopia 3 years later. bilateral blepharoptosis, external ophthalmoparesis with diplopia on horizontal gaze, dysarthria and dysphagia at 44. distal limb muscles weakness, with depressed deep tendon reflexes, and impaired proprioception and vibration sense. Positive Romberg sign. axonal sensory polyneuropath, SANDO. parkinsonism, with hand rest tremor, moderate limb bradykinesia, cogwheel rigidity and hypomimic face. Multiple mtDNA deletions were detected. | | Mutations: | P648R, R807C | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 39, Age of Patient: 52, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Ferreira et al, 2011; | | Description: | Ptosis, oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy-like, pigmentary retinopathy. | | Mutations: | P587L, P648R | | SNPs: | T251I | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 59, Age of Patient: 67, Age of Death: n/a |
Back to top | Reference: | Horvath et al, 2006; | | Description: | Onset at 25 years with PEO, ataxia, dysphagia, myopathy, and thyroid disease. | | Mutations: | P648R, P648R | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 25, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Horvath et al, 2006; | | Description: | Onset at 53 years with PEO, neuropathy. | | Mutations: | P648R, R1096C | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 53, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Ferreira et al, 2011; | | Description: | Parkinsons. Slowly progressive bilateral blepharoptosis, external ophthalmoplegia, dysphagia and dysarthria, presented with right-dominant parkinsonian features at age 56, comprising hand and lower limb rest tremor, mild upper limb cogwheel rigidity, right foot dystonic movements, hypomimic face and postural instability. impairment of vibration and pinprick sensations in glove-stocking distribution and absence of lower limb tendon reflexes. decline in attention and visuospatial functions. Axonal sensory polyneuropathy. ragged red fibers, multiple mtDNA deletions, | | Mutations: | P648R, PNF | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 56, Age of Patient: 64, Age of Death: n/a |
|
| R807C | | | | Number of patients: (with R807C) | 5 | | Found together with: | |  | Show Patient Data |
| Patient data are sorted by mutation combination frequency. | Reference: | Ferreira et al, 2011; | | Description: | Onset at 39 years with SANDO. | | Mutations: | P648R, R807C | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 39, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Gago et al, 2006; | | Description: | Man presented at age 39 progressive bilateral ptosis, unsteadiness gait and muscle weakness with difficulty in dressing and lifting objects. Three years later he noticed dysphagia and diplopia and sought medical advice. Neurological examination revealed droopy eyes which worsened after repeated eye movements and external ophthalmoparesis with diplopia on horizontal gaze. The patient also presented fluctuant dysarthria and dysphagia which worsened at the end of the day. There was distal limb muscles weakness with reduced deep tendon reflexes. Perception of vibration and position was absent below the iliac crests. Touch, pain and temperature senses were preserved. Signs of cerebellar dysfunction were also evident. Romberg sign was positive. multiple mtDNA deletions in muscle Summary: Sensory ataxia with neuropathy, dysarthria and ophthalmoparesis represent the clinical triad of SANDO | | Mutations: | P648R, R807C | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 39, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: 44 |
| Reference: | Miguel et al, 2014; | | Description: | progressive bilateral ptosis, unsteadiness gait and muscles weakness at the age of 39 and developed dysphagia and diplopia 3 years later. bilateral blepharoptosis, external ophthalmoparesis with diplopia on horizontal gaze, dysarthria and dysphagia at 44. distal limb muscles weakness, with depressed deep tendon reflexes, and impaired proprioception and vibration sense. Positive Romberg sign. axonal sensory polyneuropath, SANDO. parkinsonism, with hand rest tremor, moderate limb bradykinesia, cogwheel rigidity and hypomimic face. Multiple mtDNA deletions were detected. | | Mutations: | P648R, R807C | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 39, Age of Patient: 52, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Tang et al, 2011; | | Description: | Encephalopathy/dementia, liver failure, cholestasis, lactic acidosis, altered mental status. 47% mtDNA copy number in muscle, 8% mtDNA copy number in liver, ETC low. | | Mutations: | A467T, R807C | | Age group: | infantile | | Age of Onset: n/a, Age of Patient: 1, Age of Death: n/a |
Back to top | Reference: | Isohanni et al, 2011; | | Description: | epilepsy, vomiting, lowered consciousness, partial status epilepticus, epilepsia partialis continua, myoclonus, pschomotor regression, liver failure before valproate treatment, death via pneumonia. 72-76% mtDNA copy number in muscle. | | Mutations: | R807C, W748S | | SNPs: | E1143G | | Age group: | infantile | | Age of Onset: 1, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: 3 |
|
|
|
|
|
The following information is based on existing patient data and pathogenic cluster assignment.
Pathogenicity information for a patient with mutations in Clusters 3 and 5: Age of onset information is extracted from a total of 15 patients and/ or patient families. | Age of onset | | |
15- 8- | 3
| 3
| 0
| 9
| | | infantile | childhd | juvenile | adult | | | 20% | 20% | 0% | 60% | |
All mutations mapping within the pathogenic clusters are at high risk for pathogenicity. In general, a patient must have a pathogenic mutation in both of his/ her POLG genes to develop a POLG-related syndrome.  | Symptoms described in patients with cluster5-cluster3 mutations | |
| Symptoms in patients with combination
cluster3:cluster5 | | PEO | 53.3% | | Ptosis | 40.0% | | Epilepsy | 26.7% | | Movement disorder (ataxia) | 26.7% | | Dysarthria | 26.7% | | Encephalopathy | 20.0% | | Dysphagia | 20.0% | | Lactic acidosis | 13.3% | | Status epilepticus | 13.3% | | Peripheral neuropathy | 13.3% | | Muscle weakness | 13.3% | | Myopathy | 13.3% | | Diplopia | 13.3% | | Developmental delay | 13.3% | | No known symptoms | 6.7% | | Myoclonic seizures | 6.7% | | Hemiparesis | 6.7% | | Focal seizures | 6.7% | | Epilepsia partialis | 6.7% | | Cerebellar ataxia | 6.7% | | Cerebellar atrophy | 6.7% | | Sensory ataxia | 6.7% | | Ragged red fibers | 6.7% | | Mitochondrial myopathy | 6.7% | | Ophthalmoplegia | 6.7% | | Stroke | 6.7% | | Parkinson's disease | 6.7% | | Liver failure | 6.7% | | Liver dysfunction | 6.7% | | Headache/ migraine | 6.7% | | Psychomotor delay | 6.7% | | Retardation | 6.7% | | Pschomotor regression | 6.7% | | Lowered consciousness | 6.7% | | Vomiting | 6.7% | | Cortical blindness | 6.7% | | Distal muscle wasting | 6.7% | | Stroke-like episodes | 6.7% | | Tremor | 6.7% |
| | Data gathered from clinical descriptions for 15 patients |
| Symptoms by group | | CPEO | 60.0% | | Seizures | 40.0% | | CNS symptoms | 33.3% | | Developmental Delay | 33.3% | | Ataxia | 26.7% | | Myopathy | 26.7% | | Hepatopathy | 20.0% | | Alpers syndrome | 13.3% | | Neuropathy | 13.3% | | Other | 13.3% | | GI symptoms | 6.7% | | Migraines | 6.7% | | Unknown | 6.7% |
| | [Show grouping information] |
|
|
|