Mutation Query
| | | | Allele 1: | Q1236H, R1096C | | Allele 2: | Q1236H, R1096C | Allelic information known | | Refine query |
|
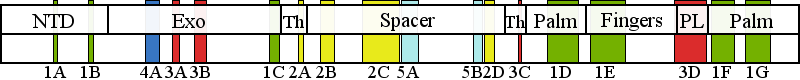
| | | Residue R1096 | | Cluster assignment: | | | Cluster description: | Partitioning loop | | Subcluster: | 3D (residues 1047-1096) | | Subcluster description: | The partitioning loop, which is a novel structural module conserved in PolG (residues 1050-1095) that is located between the fingers and palm subdomains of the pol domain, and is not present in any other known DNA polymerase (Euro et al, 2011). | | POLG domain: | Polymerase domain |
| Residue R1096 | | Cluster assignment: | | | Cluster description: | Partitioning loop | | Subcluster: | 3D (residues 1047-1096) | | Subcluster description: | The partitioning loop, which is a novel structural module conserved in PolG (residues 1050-1095) that is located between the fingers and palm subdomains of the pol domain, and is not present in any other known DNA polymerase (Euro et al, 2011). | | POLG domain: | Polymerase domain |
| Residue Q1236 | | Cluster assignment: | | | Cluster description: | Single Nucleotide Polymorphism | | POLG domain: | Polymerase domain |
| Residue Q1236 | | Cluster assignment: | | | Cluster description: | Single Nucleotide Polymorphism | | POLG domain: | Polymerase domain |
|
|
Mutation Information
|
| Q1236H | | | | Number of patients: (with Q1236H) | 12 | | Found together with: | PNF=Putatively Non-Functional enzyme |  | Show Patient Data |
| Patient data are sorted by mutation combination frequency. | Reference: | Horvath et al, 2006; | | Description: | Onset at 2 years with encephalopathy, hepatopathy, and myoclonus achalasia. Diagnosed as Alpers. | | Mutations: | R1096C, R1096C | | SNPs: | Q1236H, Q1236H | | Age group: | infantile | | Age of Onset: 2, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Wong et al, 2008; | | Description: | developmental delay, dementia, seizures, Alpers, Family history of Alpers syndrome. | | Mutations: | R1096C, R1096C | | SNPs: | Q1236H, Q1236H | | Age group: | infantile | | Age of Onset: 1, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Luoma et al, 2005; | | Description: | Developed bilateral blepharoptosis in his youth. Neurological examination at the age of 72 showed severe blepharoptosis, lids almost covering his entire pupils. Eye movements were normal, his muscle strength and sensation were good and tendon reflexes were normal, but his gait was unsteady. Early onset ptosis, ataxia | | Mutations: | R627Q | | SNPs: | Q1236H | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 22, Age of Patient: 73, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Luoma et al, 2005; | | Description: | developed progressive blepharoptosis at the age of 20 and ophthalmoplegia during subsequent years, at 35, the patient developed progressive unsteadiness of gait. She noted fatigue, myalgia and cramps, which were triggered by moderate exercise. At 44, restless legs syndrome, deficits in memory and concentration, and suffered from recurrent episodes of depression, at 46 showed bilateral blepharoptosis, limited eye movements in all directions except downwards, lateral rotatory nystagmus and slight upbeat nystagmus in upward gaze, but no saccades. She had facial muscle weakness, dysarthria and slight proximal muscle weakness. She had glove and stockinglike hypoesthesia, distally impaired vibration sense, absent ankle reflexes and weak other tendon reflexes, as well as mild dysmetria. Her gait was broad-based, with further impairment with eyes closed. Tandem gait was impaired. deltoid muscle showed myopathic features, structurally abnormal mitochondria with para-crystalline inclusions, | | Mutations: | A467T, R627Q | | SNPs: | Q1236H | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 20, Age of Patient: 46, Age of Death: n/a |
Back to top | Reference: | Luoma et al, 2005; | | Description: | displays mild bilateral blepharoptosis and slight unsteadiness during tandem gait. Early onset ptosis, ataxia | | Mutations: | R627Q | | SNPs: | Q1236H | | Age group: | juvenile | | Age of Onset: n/a, Age of Patient: 19, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Zabalza et al, 2014; | | Description: | Unsteady walk, and showed tremor in both legs when standing. Difficulty in concentrating. Dysarthria. No deep tendon reflexes were evident. Sensory axonal neuropathy. Hyperintensities in images of the subcortical frontal and temporal white substances. myoclonia and tonic-clonic seizures. sensory axonal neuropathy in the lower limbs, moderate dysarthria, and an ataxic gait. | | Mutations: | K601E | | SNPs: | D122Y, Q1236H, Y837C | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 56, Age of Patient: 61, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Zabalza et al, 2014; | | Description: | ataxia, dysarthria and sensory axonal polyneuropathy. At age 52, the patient developed instability upon walking and paraesthesia in lower limbs, when no other symptoms were apparent. Clinical examination at age 67 revealed dysarthria, gait ataxia, hyporeflexia and tactile hypoestesia. Atrophy of the cerebellar hemispheres. Cognitive decline. left hemiparesis related to a non-traumatic subdural haematoma that required neurosurgical treatment, and began to experience myoclonus and tonic-clonic seizures. weak bilateral palpebral ptosis. | | Mutations: | K601E | | SNPs: | D122Y, Q1236H, Y837C | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 52, Age of Patient: 67, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Taanman et al, 2009; | | Description: | Hypotonia at 8 weeks, seizures, hepatopathy, lactic acidemia, died of liver failure. 9% mtDNA copy number in muscle, 11% mtDNA copy number in liver. | | Mutations: | H1110Y, W748S | | SNPs: | E1143G, Q1236H | | Age group: | infantile | | Age of Onset: 0.1, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: 0.8 |
| Reference: | Pagnamenta et al, 2006; | | Description: | Presented with ptosis and PEO, in early 20’s, premature ovarian failure at 28 years. proximal muscle weakness, exertional dyspnoea and sensory ataxia, Peripheral neuropathy | | Mutations: | Y955C | | SNPs: | Q1236H | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 22, Age of Patient: 33, Age of Death: n/a |
Back to top | Reference: | Luoma et al, 2007; | | Description: | Parkinsons disease, tremor, rigidity, hypo-/ bradykinesia. | | Mutations: | | | SNPs: | Q1236H, R722H | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 66, Age of Patient: 77, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Luoma et al, 2007; | | Description: | Parkinsons disease, tremor, rigidity, hypo-/ bradykinesia. Ischemic Heart Disease, atrial fibrillation, hypertension | | Mutations: | | | SNPs: | Q1236H, Y831C | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 70, Age of Patient: 79, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Wong et al, 2008; | | Description: | Alpers, chorea, microcephaly, leukodystrophy, Seizures, Dementia, developmental delay. | | Mutations: | A467T | | SNPs: | PNF, Q1236H | | Age group: | infantile | | Age of Onset: 1.5, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: n/a |
|
| R1096C | | | | Number of patients: (with R1096C) | 15 | | Found as the only mutation: | 7% of entries (1 patient) | | Found together with: | |  | Show Patient Data |
| Patient data are sorted by mutation combination frequency. | Reference: | Ashley et al, 2008; | | Description: | Epilepsy, Cellular depletion, Hepatopathy | | Mutations: | R1096C, R1096C | | Age group: | infantile | | Age of Onset: 0.42, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Horvath et al, 2006; | | Description: | Onset at 2 years with encephalopathy, hepatopathy, and myoclonus achalasia. Diagnosed as Alpers. | | Mutations: | R1096C, R1096C | | SNPs: | Q1236H, Q1236H | | Age group: | infantile | | Age of Onset: 2, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Tang et al, 2011; | | Description: | Developmental delay, seizure, lactic acidosis, elevated transaminases. 50% mtDNA copy number in blood. | | Mutations: | R1096C, R1096C | | Age group: | infantile | | Age of Onset: n/a, Age of Patient: 2, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Tang et al, 2011; | | Description: | Seizures, dementia/encephalopathy. 56% mtDNA copy number in blood. | | Mutations: | R1096C, R1096C | | Age group: | infantile | | Age of Onset: n/a, Age of Patient: 0.8, Age of Death: n/a |
Back to top | Reference: | Tang et al, 2011; | | Description: | Seizures, liver failure. | | Mutations: | R1096C, R1096C | | Age group: | infantile | | Age of Onset: n/a, Age of Patient: 1, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Wong et al, 2008; | | Description: | developmental delay, dementia, seizures, Alpers, Family history of Alpers syndrome. | | Mutations: | R1096C, R1096C | | SNPs: | Q1236H, Q1236H | | Age group: | infantile | | Age of Onset: 1, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Bijarnia-Mahay et al, 2014; | | Description: | altered sensorium, seizures (requiring ventilation and critical-care management), hypotonia and mild hepatomegaly. Child deteriorated rapidly because of liver failure and died within two weeks of admission. Mainly hepatic failure and central nervous system (CNS) involvement (encephalopathy, seizures), high plasma lactate levels – and family history, a clinical diagnosis of mitochondrial disorder of the mtDNA depletion (Alpers – Huttenlocher syndrome or Pyruvate carboxylase deficiency) was made. mtDNA depletion syndrome. | | Mutations: | R1096C, R1096C | | Age group: | infantile | | Age of Onset: 0.3, Age of Patient: 0.6, Age of Death: 0.6 |
| Reference: | Stewart et al, 2011; | | Description: | Alpers. Multifocal therapy-refractory epilepsy. hippocampal sclerosis. COX-negative fibers, reduced mtDNA copy number. mtDNA deletions. | | Mutations: | R1096C, R1096C | | Age group: | infantile | | Age of Onset: n/a, Age of Patient: 1, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Horvath et al, 2006; | | Description: | Onset at 53 years with PEO, neuropathy. | | Mutations: | P648R, R1096C | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 53, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: n/a |
Back to top | Reference: | Tang et al, 2011; | | Description: | Developmental delay, hypotonia, dementia/encephalopathy, exercise intolerance, muscle weakness, easy fatigability, ptosis, GI reflux, delayed gastric emptying, cyclic vomiting, hepatic failure, elevated transaminases, lactic acidosis, short statue, FTT. 53% mtDNA copy number in blood. | | Mutations: | G848S, R1096C | | Age group: | infantile | | Age of Onset: n/a, Age of Patient: 2, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Ashley et al, 2008; | | Description: | reported as Alpers, onset at <1 year, presenting encephalopathy with epilepsy, hepatopathy, and movement disorder (ataxia). 7% mtDNA copy number in liver, 23% mtDNA copy number in muscle | | Mutations: | R1096C, T914P | | Age group: | infantile | | Age of Onset: 1, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Lax et al, 2012a; | | Description: | CPEO, Ptosis, Peripheral neuropathy, COX-deficient fibers, ragged red fibers, presence of mitochondrial dna deletions in muscle, Sensory and motor neuronopathy, Distal and proximal neurogenic change | | Mutations: | A467T, R1096C | | Age group: | juvenile | | Age of Onset: 17, Age of Patient: 42, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Lax et al, 2012a; | | Description: | CPEO, Ptosis, Peripheral neuropathy, COX-deficient fibers, ragged red fibers, presence of mitochondrial dna deletions in muscle, epilepsy, Severe sensory and moderate motor neuronopathy, Distal neurogenic change, proximal myopathy | | Mutations: | R1096C, W748S | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 25, Age of Patient: 49, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Kurt et al, 2012; | | Description: | sensory ataxic neuropathy, dysarthria, ophthalmoplegia, and dysphagia. At the age of 41, progressive diplopia and ptosis were added to the symptoms. Five years later, she gradually had dysarthria and restless leg syndrome. ragged red fibers. | | Mutations: | L591F, R1096C | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 38, Age of Patient: 48, Age of Death: n/a |
Back to top | Reference: | Agostino et al, 2003; | | Description: | PEO, bilateral ptosis, severe limitation of ocular motility, and a mosaic distribution of ragged-red and cytochrome c oxidase negative fibers in the muscle biopsy. All patients had multiple deletions of muscle mtDNA. | | Mutations: | R1096C | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 23, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: n/a |
|
|
|
|
|
The following information is based on existing patient data and pathogenic cluster assignment.
Pathogenicity information for a patient with mutations in Clusters 3 and 3: Age of onset information is extracted from a total of 21 patients and/ or patient families. | Age of onset | | |
21- 11- | 10
| 6
| 2
| 3
| | | infantile | childhd | juvenile | adult | | | 48% | 29% | 10% | 14% | |
All mutations mapping within the pathogenic clusters are at high risk for pathogenicity. In general, a patient must have a pathogenic mutation in both of his/ her POLG genes to develop a POLG-related syndrome.  | Symptoms described in patients with cluster3-cluster3 mutations | |
| Symptoms in patients with combination
cluster3:cluster3 | | PEO | 42.9% | | Epilepsy | 33.3% | | Ptosis | 33.3% | | Encephalopathy | 33.3% | | Developmental delay | 33.3% | | Lactic acidosis | 23.8% | | Movement disorder (ataxia) | 19.0% | | Peripheral neuropathy | 19.0% | | Muscle weakness | 19.0% | | Ragged red fibers | 14.3% | | Exercise intolerance | 14.3% | | Dysphagia | 14.3% | | Myoclonic seizures | 9.5% | | Polyneuropathy | 9.5% | | Abnormal muscle histology | 9.5% | | Myopathy | 9.5% | | Liver failure | 9.5% | | Hypotonic | 9.5% | | Dementia | 9.5% | | CPK abnormalities | 9.5% | | +9 other symptoms in under 5.0% of the patients |
| | Data gathered from clinical descriptions for 21 patients |
| Symptoms by group | | CPEO | 52.4% | | Developmental Delay | 42.9% | | Myopathy | 42.9% | | Seizures | 38.1% | | Hepatopathy | 33.3% | | Neuropathy | 28.6% | | Alpers syndrome | 23.8% | | CNS symptoms | 23.8% | | Ataxia | 19.0% | | Hypotonia | 9.5% | | Other | 9.5% | | Unknown | 4.8% |
| | [Show grouping information] |
|
|
|