Mutation Query
| | | | Allele 1: | A962T | | Allele 2: | R964C | Allelic information known | | Refine query |
|
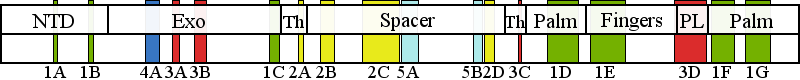
| | | Residue A962 | | Cluster assignment: | | | Cluster description: | Polymerase active site and environs | | Subcluster: | 1E (residues 914-966) | | Subcluster description: | This subcluster comprises most of the fingers subdomain of the pol domain, including the O-helix and the Pol B motif (Loh and Loeb, 2005). | | POLG domain: | Polymerase domain |
| Residue R964 | | Cluster assignment: | | | Cluster description: | Polymerase active site and environs | | Subcluster: | 1E (residues 914-966) | | Subcluster description: | This subcluster comprises most of the fingers subdomain of the pol domain, including the O-helix and the Pol B motif (Loh and Loeb, 2005). | | POLG domain: | Polymerase domain |
|
|
Mutation Information
|
| A962T | | | | Number of patients: (with A962T) | 1 | | Non-allelic with: | R964C (100%) |  | Show Patient Data |
| Patient data are sorted by mutation combination frequency. | Reference: | Tang et al, 2011; | | Description: | Ataxia, muscle weakness, central hypoventilation. 119% mtDNA copy number in blood. | | Mutations: | A962T, R964C | | Age group: | juvenile | | Age of Onset: n/a, Age of Patient: 14, Age of Death: n/a |
|
| R964C | | | | Number of patients: (with R964C) | 5 | | Found together with: | |  | Show Patient Data |
| Patient data are sorted by mutation combination frequency. | Reference: | Stricker et al, 2009; | | Description: | Progressive cerebellar ataxia, neuropathy, restless legs syndrome, hemihypesthia, myoclonic epileptic seizures, severe ataxia, dysphagia, muscle strength preserved, migraines, headaches, abdominal pain, death via prolonged status epilepticus. | | Mutations: | A862T, R964C | | Age group: | juvenile | | Age of Onset: 15, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: 27 |
| Reference: | Stricker et al, 2009; | | Description: | Progressively focal motor and tonic-clonic seizures, delayed psychomotor development, sensoriaxonal neuropathy, mild tetraparesis, cerebellar syndrome, intestinal pseudoobstruction, died via refractory status epilepticus. | | Mutations: | A862T, R964C | | Age group: | childhood | | Age of Onset: 5, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: 23 |
| Reference: | Wong et al, 2008; | | Description: | Onset 17 years with ataxia, exercise intolerance, cerbellar atrophy, SCAE, seizures, dementia. | | Mutations: | A862T, R964C | | Age group: | juvenile | | Age of Onset: 17, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Tang et al, 2011; | | Description: | Ataxia, muscle weakness, central hypoventilation. 119% mtDNA copy number in blood. | | Mutations: | A962T, R964C | | Age group: | juvenile | | Age of Onset: n/a, Age of Patient: 14, Age of Death: n/a |
Back to top | Reference: | Yamanaka et al, 2007; | | Description: | 34-year-old HIV-1–infected Thai woman who had been asymptomatic until the development of Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia. She had suffered from severe lactic acidosis after 1 year of use of d4T and lamivudine (3TC). Her peak lactate level was 67 mg/dL, and paresthesia was still present in both legs after 15 years of cessation of d4T treatment. Severe lactic acidosis induced by 1 year of treatment with d4T. | | Mutations: | R964C, R964C | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: n/a, Age of Patient: 34, Age of Death: n/a |
|
|
|
|
|
The following information is based on existing patient data and pathogenic cluster assignment.
Pathogenicity information for a patient with mutations in Clusters 1 and 1: Age of onset information is extracted from a total of 20 patients and/ or patient families. | Age of onset | | |
20- 10- | 2
| 7
| 3
| 8
| | | infantile | childhd | juvenile | adult | | | 10% | 35% | 15% | 40% | |
All mutations mapping within the pathogenic clusters are at high risk for pathogenicity. In general, a patient must have a pathogenic mutation in both of his/ her POLG genes to develop a POLG-related syndrome.  | Symptoms described in patients with cluster1-cluster1 mutations | |
| Symptoms in patients with combination
cluster1:cluster1 | | Developmental delay | 30.0% | | Movement disorder (ataxia) | 25.0% | | PEO | 25.0% | | Muscle weakness | 20.0% | | Hypotonic | 20.0% | | Dementia | 20.0% | | Status epilepticus | 15.0% | | Myopathy | 15.0% | | Ophthalmoplegia | 15.0% | | Liver failure | 15.0% | | Failure to thrive | 15.0% | | Tremor | 15.0% | | Lactic acidosis | 10.0% | | Peripheral neuropathy | 10.0% | | Ptosis | 10.0% | | Encephalopathy | 10.0% | | Vomiting | 10.0% | | Dysphagia | 10.0% | | Hepatomegaly | 10.0% | | Hearing loss | 10.0% | | No known symptoms | 5.0% | | Myoclonic seizures | 5.0% | | Hemiparesis | 5.0% | | Intractable seizure | 5.0% | | Epilepsy | 5.0% | | Cerebellar ataxia | 5.0% | | Polyneuropathy | 5.0% | | Demyelinating neuropathy | 5.0% | | Sensomotor neuropathy | 5.0% | | Exercise intolerance | 5.0% | | Parkinson's disease | 5.0% | | Jaundice | 5.0% | | Headache/ migraine | 5.0% | | Delayed gastric emptying | 5.0% | | Cortical blindness | 5.0% | | Dysarthria | 5.0% | | Respiratory deficiency | 5.0% | | Leigh syndrome | 5.0% | | Areflexia | 5.0% | | CPK abnormalities | 5.0% | | Hypoglycemia | 5.0% |
| | Data gathered from clinical descriptions for 20 patients |
| Symptoms by group | | Developmental Delay | 40.0% | | Myopathy | 35.0% | | Seizures | 35.0% | | CPEO | 30.0% | | Ataxia | 25.0% | | CNS symptoms | 25.0% | | Hepatopathy | 25.0% | | Neuropathy | 25.0% | | Other | 25.0% | | Hypotonia | 20.0% | | GI symptoms | 15.0% | | Alpers syndrome | 5.0% | | Migraines | 5.0% | | Unknown | 5.0% |
| | [Show grouping information] |
|
|
|