Mutation Query
| | | | Allele 1: | A862T | | Allele 2: | R964C | Allelic information known | | Refine query |
|
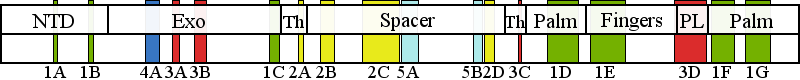
| | | Residue A862 | | Cluster assignment: | | | Cluster description: | Polymerase active site and environs | | Subcluster: | 1D (residues 848-895) | | Subcluster description: | This subcluster forms a large portion of the pol active site and contains two highly conserved motifs that are found in all family A polymerases: the RR loop (motif 2) and motif A (Loh and Loeb, 2005). | | POLG domain: | Polymerase domain |
| Residue R964 | | Cluster assignment: | | | Cluster description: | Polymerase active site and environs | | Subcluster: | 1E (residues 914-966) | | Subcluster description: | This subcluster comprises most of the fingers subdomain of the pol domain, including the O-helix and the Pol B motif (Loh and Loeb, 2005). | | POLG domain: | Polymerase domain |
|
|
Mutation Information
|
| A862T | | | | Number of patients: (with A862T) | 7 | | Found together with: | |  | Show Patient Data |
| Patient data are sorted by mutation combination frequency. | Reference: | Stricker et al, 2009; | | Description: | Progressive cerebellar ataxia, neuropathy, restless legs syndrome, hemihypesthia, myoclonic epileptic seizures, severe ataxia, dysphagia, muscle strength preserved, migraines, headaches, abdominal pain, death via prolonged status epilepticus. | | Mutations: | A862T, R964C | | Age group: | juvenile | | Age of Onset: 15, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: 27 |
| Reference: | Stricker et al, 2009; | | Description: | Progressively focal motor and tonic-clonic seizures, delayed psychomotor development, sensoriaxonal neuropathy, mild tetraparesis, cerebellar syndrome, intestinal pseudoobstruction, died via refractory status epilepticus. | | Mutations: | A862T, R964C | | Age group: | childhood | | Age of Onset: 5, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: 23 |
| Reference: | Wong et al, 2008; | | Description: | Onset 17 years with ataxia, exercise intolerance, cerbellar atrophy, SCAE, seizures, dementia. | | Mutations: | A862T, R964C | | Age group: | juvenile | | Age of Onset: 17, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Stewart et al, 2009; | | Description: | PEO with ataxia, SCA-like phenotype in siblings, multiple deletions in muscle mtDNA detected via LPCR. 3% COX deficient fibers. | | Mutations: | A862T, R1047W | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 61, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: n/a |
Back to top | Reference: | Lax et al, 2012a; | | Description: | CPEO, Ptosis, Peripheral neuropathy, COX-deficient fibers, presence of mitochondrial dna deletions in muscle, ataxia, dysarthria, Axonal sensory neuropathy /neuronopathy, Distal and proximal neurogenic change. | | Mutations: | A862T, R1047W | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 22, Age of Patient: 61, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Ferreira et al, 2011; | | Description: | Onset at 2.5 years with epilepsy, diagnosed as Alpers. Complex IV 33%. showed psychomotor regression around age 2.5 years, and developed repetitive generalized tonic–clonic seizures. Myoclonic jerks. | | Mutations: | A862T, R1081Q | | Age group: | childhood | | Age of Onset: 3, Age of Patient: 7, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | McKelvie et al, 2012; | | Description: | Ataxia, sensory ataxic neuropathy, with cerebellar features, visual disturbances with diplopia, dysarthria and dysphasia. Multiple mtDNA seletions, COX-negative fibers and ragged red fibers were found in autopsy. Areflexic, absent reflexes, in all limbs, distal weakness and distal sensory loss of proprioception and vibration. She became encephalopathic and febrile. | | Mutations: | A862T, H277L | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 46, Age of Patient: 54, Age of Death: 66 |
|
| R964C | | | | Number of patients: (with R964C) | 5 | | Found together with: | |  | Show Patient Data |
| Patient data are sorted by mutation combination frequency. | Reference: | Stricker et al, 2009; | | Description: | Progressive cerebellar ataxia, neuropathy, restless legs syndrome, hemihypesthia, myoclonic epileptic seizures, severe ataxia, dysphagia, muscle strength preserved, migraines, headaches, abdominal pain, death via prolonged status epilepticus. | | Mutations: | A862T, R964C | | Age group: | juvenile | | Age of Onset: 15, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: 27 |
| Reference: | Stricker et al, 2009; | | Description: | Progressively focal motor and tonic-clonic seizures, delayed psychomotor development, sensoriaxonal neuropathy, mild tetraparesis, cerebellar syndrome, intestinal pseudoobstruction, died via refractory status epilepticus. | | Mutations: | A862T, R964C | | Age group: | childhood | | Age of Onset: 5, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: 23 |
| Reference: | Wong et al, 2008; | | Description: | Onset 17 years with ataxia, exercise intolerance, cerbellar atrophy, SCAE, seizures, dementia. | | Mutations: | A862T, R964C | | Age group: | juvenile | | Age of Onset: 17, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Tang et al, 2011; | | Description: | Ataxia, muscle weakness, central hypoventilation. 119% mtDNA copy number in blood. | | Mutations: | A962T, R964C | | Age group: | juvenile | | Age of Onset: n/a, Age of Patient: 14, Age of Death: n/a |
Back to top | Reference: | Yamanaka et al, 2007; | | Description: | 34-year-old HIV-1–infected Thai woman who had been asymptomatic until the development of Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia. She had suffered from severe lactic acidosis after 1 year of use of d4T and lamivudine (3TC). Her peak lactate level was 67 mg/dL, and paresthesia was still present in both legs after 15 years of cessation of d4T treatment. Severe lactic acidosis induced by 1 year of treatment with d4T. | | Mutations: | R964C, R964C | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: n/a, Age of Patient: 34, Age of Death: n/a |
|
|
|
|
|
The following information is based on existing patient data and pathogenic cluster assignment.
Pathogenicity information for a patient with mutations in Clusters 1 and 1: Age of onset information is extracted from a total of 20 patients and/ or patient families. | Age of onset | | |
20- 10- | 2
| 7
| 3
| 8
| | | infantile | childhd | juvenile | adult | | | 10% | 35% | 15% | 40% | |
All mutations mapping within the pathogenic clusters are at high risk for pathogenicity. In general, a patient must have a pathogenic mutation in both of his/ her POLG genes to develop a POLG-related syndrome.  | Symptoms described in patients with cluster1-cluster1 mutations | |
| Symptoms in patients with combination
cluster1:cluster1 | | Developmental delay | 30.0% | | Movement disorder (ataxia) | 25.0% | | PEO | 25.0% | | Muscle weakness | 20.0% | | Hypotonic | 20.0% | | Dementia | 20.0% | | Status epilepticus | 15.0% | | Myopathy | 15.0% | | Ophthalmoplegia | 15.0% | | Liver failure | 15.0% | | Failure to thrive | 15.0% | | Tremor | 15.0% | | Lactic acidosis | 10.0% | | Peripheral neuropathy | 10.0% | | Ptosis | 10.0% | | Encephalopathy | 10.0% | | Vomiting | 10.0% | | Dysphagia | 10.0% | | Hepatomegaly | 10.0% | | Hearing loss | 10.0% | | No known symptoms | 5.0% | | Myoclonic seizures | 5.0% | | Hemiparesis | 5.0% | | Intractable seizure | 5.0% | | Epilepsy | 5.0% | | Cerebellar ataxia | 5.0% | | Polyneuropathy | 5.0% | | Demyelinating neuropathy | 5.0% | | Sensomotor neuropathy | 5.0% | | Exercise intolerance | 5.0% | | Parkinson's disease | 5.0% | | Jaundice | 5.0% | | Headache/ migraine | 5.0% | | Delayed gastric emptying | 5.0% | | Cortical blindness | 5.0% | | Dysarthria | 5.0% | | Respiratory deficiency | 5.0% | | Leigh syndrome | 5.0% | | Areflexia | 5.0% | | CPK abnormalities | 5.0% | | Hypoglycemia | 5.0% |
| | Data gathered from clinical descriptions for 20 patients |
| Symptoms by group | | Developmental Delay | 40.0% | | Myopathy | 35.0% | | Seizures | 35.0% | | CPEO | 30.0% | | Ataxia | 25.0% | | CNS symptoms | 25.0% | | Hepatopathy | 25.0% | | Neuropathy | 25.0% | | Other | 25.0% | | Hypotonia | 20.0% | | GI symptoms | 15.0% | | Alpers syndrome | 5.0% | | Migraines | 5.0% | | Unknown | 5.0% |
| | [Show grouping information] |
|
|
|