Mutation Query
| | | | Allele 1: | R232H, S64L | | Allele 2: | G737R | Allelic information known | | Refine query |
|
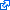
| | | Residue S64 | | Cluster assignment: | | | Cluster description: | Single Nucleotide Polymorphism | | POLG domain: | N-Terminal domain |
| Residue R232 | | Cluster assignment: | | | Cluster description: | Distal accessory subunit interface | | Subcluster: | 4A (residues 224-244) | | Subcluster description: | These mutations map to the exo domain along the distal accessory subunit interface. | | POLG domain: | Exonuclease domain |
| Residue G737 | | Cluster assignment: | | | Cluster description: | Putative protein-protein interactions | | Subcluster: | 5B (residues 737-749) | | Subcluster description: | Located in the periphery of the IP subdomain of the spacer domain, distant from the DNA binding channel | | POLG domain: | Spacer domain |
|
|
Mutation Information
|
| R232H | | | | Number of patients: (with R232H) | 8 | | Found as the only mutation: | 38% of entries (3 patients) | | Found together with: | |  | Show Patient Data |
| Patient data are sorted by mutation combination frequency. | Reference: | Rouzier et al, 2013; | | Description: | Axonal sensorimotor neuropathy | | Mutations: | R232H | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 30, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Rouzier et al, 2013; | | Description: | Axonal sensorimotor neuropathy, sensory ataxia, parkinsonism. | | Mutations: | R232H | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 25, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Rouzier et al, 2013; | | Description: | Axonal sensorimotor neuropathy, sensory ataxia. Very mild axonal neuropathy identified in this patient's daughter. | | Mutations: | R232H | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 20, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Hunter et al, 2011; | | Description: | Developmental Delay or Regression, hypotonia, vomiting, Abnormal Liver Enzymes, liver mtDNA depletion, clinical diagnosis of infantile hepatopathy | | Mutations: | A467T, H277L, R232H | | Age group: | infantile | | Age of Onset: 0.125, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: 0.25 |
Back to top | Reference: | Hunter et al, 2011; | | Description: | Developmental Delay or Regression, motor paresis, hypotonia, vomiting, Abnormal Liver Enzymes, Serum Lactate, liver mtDNA depletion, clinical diagnosis of infantile hepatopathy | | Mutations: | A467T, H277L, R232H | | Age group: | infantile | | Age of Onset: 0.17, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: 0.25 |
| Reference: | Taanman et al, 2009; | | Description: | Hypotonia, microcephaly, abnormal MRI, hepatomegaly, FTT, hypoglycaemia, ptosis. Onset at 6 months with Leighs syndrome and death at 23 months. 3% mtDNA copy number in muscle and 12% mtDNA copy number in liver. | | Mutations: | G848S, R232H | | Age group: | infantile | | Age of Onset: 0.5, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: 2 |
| Reference: | Kollberg et al, 2006; | | Description: | Alpers, age of onset 6 months, age of death 13 months. 41% mtDNA copy number. During the first 6 months of life, he was considered healthy, but was irritable with colic-like symptoms. failure to thrive, delayed motor development. myoclonus. leftsided hemiparesis. | | Mutations: | R232H, W748S | | SNPs: | E1143G | | Age group: | infantile | | Age of Onset: 0.5, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: 1.08 |
| Reference: | Harrower et al, 2008; | | Description: | Peripheral neuropathy, tremor, ataxia. | | Mutations: | G737R, R232H | | SNPs: | S64L | | Age group: | childhood | | Age of Onset: 10, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: n/a |
|
| S64L | | | | Number of patients: (with S64L) | 1 | | Allelic with: | R232H (100%) | | Non-allelic with: | G737R (100%) |  | Show Patient Data |
| Patient data are sorted by mutation combination frequency. | Reference: | Harrower et al, 2008; | | Description: | Peripheral neuropathy, tremor, ataxia. | | Mutations: | G737R, R232H | | SNPs: | S64L | | Age group: | childhood | | Age of Onset: 10, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: n/a |
|
| G737R | | | | Number of patients: (with G737R) | 13 | | Found together with: | |  | Show Patient Data |
| Patient data are sorted by mutation combination frequency. | Reference: | Wong et al, 2008; | | Description: | Onset 60 years with ataxia, neuropathy, myopathy, hearing loss, cerebellar atrophy, SANDO/SCAE, PEO. | | Mutations: | A467T, G737R | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 60, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Milone et al, 2011; | | Description: | progressive sensory ataxic neuropathy, ophthalmoparesis, cerebellar ataxia, limb weakness, muscle cramps, sensory hearing loss, dysarthria, dysphagia, constipation, and memory loss, brain MRI was abnormal with evidence of generalized cortical and cerebellar atrophy, evidence of a length-dependent sensory > motor polyneuropathy of axonal type, Multiple mtDNA deletions detected by PCR in blood | | Mutations: | A467T, G737R | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 53, Age of Patient: 58, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Horvath et al, 2006; | | Description: | Onset at 0.8 years with encephalopathy, liver dysfunction, diagnosed as Alpers. Death at 1 year. | | Mutations: | A767D, G737R | | Age group: | infantile | | Age of Onset: 0.8, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: 1 |
| Reference: | Sitarz et al, 2014; | | Description: | Epilepsy, Myopathy. | | Mutations: | A767D, G737R | | Age group: | infantile | | Age of Onset: n/a, Age of Patient: 1, Age of Death: n/a |
Back to top | Reference: | Davidzon et al, 2006; | | Description: | Migraines in childhood, In 20s presented with peripheral sensory neuropathy and parkinsonisms. | | Mutations: | G737R, R853W | | Age group: | childhood | | Age of Onset: n/a, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Rempe et al, 2016; | | Description: | parkinsonism with dystonic toe and plantar flexion. Anxiety and generalized muscle weakness. Bilateral hypaesthesia of the lateral bottom of the foot and dorsal forefoot as well as bilateral distal pallhypaesthesia of the legs. Slight bilateral ptosis, slight axonal sensory polyneuropathy. | | Mutations: | G737R, R853W | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 27, Age of Patient: 32, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Harrower et al, 2008; | | Description: | Peripheral neuropathy, tremor, ataxia. | | Mutations: | G737R, R232H | | SNPs: | S64L | | Age group: | childhood | | Age of Onset: 10, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Tang et al, 2011; | | Description: | Muscle weakness, ptosis, ophthalmoparesis/CPEO. 61% mtDNA copy number in blood. | | Mutations: | G737R, L304R | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: n/a, Age of Patient: 54, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Tang et al, 2011; | | Description: | Seizures, intractable seizures, abnormal EEG, abnormal MRI. 135% mtDNA copy number in blood. | | Mutations: | G426S, G737R | | Age group: | childhood | | Age of Onset: n/a, Age of Patient: 11, Age of Death: n/a |
Back to top | Reference: | Tang et al, 2011; | | Description: | Deceased at 9 months. 30% mtDNA copy number in muscle, 30% mtDNA copy number in blood, 10% mtDNA copy number in liver. | | Mutations: | A957V, G737R | | Age group: | infantile | | Age of Onset: n/a, Age of Patient: 0.4, Age of Death: 0.8 |
| Reference: | Tang et al, 2011; | | Description: | Hypoglycaemia, liver failure, seizures, developmental delay. 65% mtDNA copy number in muscle, ETC low. | | Mutations: | G737R, V855L | | Age group: | infantile | | Age of Onset: n/a, Age of Patient: 0.8, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Wong et al, 2008; | | Description: | Onset at age 3 with dementia,lactic acidosis, renal tubulopathy, dysmorphic features, cataract, short stature, myopathy. | | Mutations: | G737R, R943C | | SNPs: | E1143G | | Age group: | childhood | | Age of Onset: 3, Age of Patient: n/a, Age of Death: n/a |
| Reference: | Tzoulis et al, 2009; | | Description: | PEO. Primary hypothyroidism and bilateral hearing loss of uncertain duration. She had been operated for bilateral ptosis at 75 years of age and presented to us with 2–3 years of worsening diplopia, gait unsteadiness and paresthaesiae in the distal lower limbs. asymmetrical ptosis and nearly complete external ophthalmoplegia with loss of convergence, oculocephalic reflex and Bell\'s reflex. She had symmetrical distal sensory loss in the lower limbs and absence of Achilles reflexes. | | Mutations: | G737R, W748S | | Age group: | adult | | Age of Onset: 75, Age of Patient: 86, Age of Death: n/a |
|
|
|
|
|
The following information is based on existing patient data and pathogenic cluster assignment.
Pathogenicity information for a patient with mutation G737R and a cluster 4 mutation: Age of onset information is extracted from a total of 1 patients and/ or patient families. | Age of onset | | |
1- 1- | 0
| 1
| 0
| 0
| | | infantile | childhd | juvenile | adult | | | 0% | 100% | 0% | 0% | |
All mutations mapping within the pathogenic clusters are at high risk for pathogenicity. In general, a patient must have a pathogenic mutation in both of his/ her POLG genes to develop a POLG-related syndrome.  | Symptoms described in patients with G737R-cluster4 mutations | | Symptoms in patients with combination
G737R:cluster4 | | Movement disorder (ataxia) | 100.0% | | Peripheral neuropathy | 100.0% | | Tremor | 100.0% |
| | Data gathered from clinical descriptions for 1 patient |
|  | Symptoms described in patients with cluster4-cluster5 mutations | |
| Symptoms in patients with combination
cluster4:cluster5 | | Myoclonic seizures | 50.0% | | Epilepsy | 50.0% | | Hemiparesis | 25.0% | | Epilepsia partialis | 25.0% | | Movement disorder (ataxia) | 25.0% | | Peripheral neuropathy | 25.0% | | Liver failure | 25.0% | | Liver dysfunction | 25.0% | | Failure to thrive | 25.0% | | Encephalopathy | 25.0% | | Developmental delay | 25.0% | | Respiratory deficiency | 25.0% | | Tremor | 25.0% |
| | Data gathered from clinical descriptions for 4 patients |
| Symptoms by group | | Hepatopathy | 50.0% | | Seizures | 50.0% | | Alpers syndrome | 25.0% | | Ataxia | 25.0% | | CNS symptoms | 25.0% | | Developmental Delay | 25.0% | | Neuropathy | 25.0% | | Other | 25.0% |
| | [Show grouping information] |
|
|
|